Machado-Joseph Disease (MJD)/Spinocerebellar Ataxia Type 3 (SCA3) via the ATXN3 CAG Repeat Expansion
Summary and Pricing 
Test Method
Combination Of Repeat-Primed PCR and Fluorescent Fragment-Length Assay| Test Code | Test Copy Genes | Test CPT Code | Gene CPT Codes Copy CPT Code | Base Price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13213 | ATXN3 | 81180 | 81180 | $350 | Order Options and Pricing |
An additional 25% charge will be applied to STAT orders. STAT orders are prioritized throughout the testing process.
Turnaround Time
3 weeks on average for standard orders or 2 weeks on average for STAT orders.
Please note: Once the testing process begins, an Estimated Report Date (ERD) range will be displayed in the portal. This is the most accurate prediction of when your report will be complete and may differ from the average TAT published on our website. About 85% of our tests will be reported within or before the ERD range. We will notify you of significant delays or holds which will impact the ERD. Learn more about turnaround times here.
Targeted Testing
For ordering sequencing of targeted known variants, go to our Targeted Variants page.
Clinical Features and Genetics 
Clinical Features
Machado-Joseph disease (MJD), also referred to as spinocerebellar ataxia type 3 (SCA3), is progressive form of cerebellar ataxia caused by expansion of the poly-glutamine tract within the ATXN3 gene. MJD/SCA3 is the most common form of adult-onset hereditary ataxia worldwide (Ruano et al. 2014. PubMed ID: 24603320). The overall incidence is estimated to be as high as 2 per 100,000 people globally; however, the incidence is significantly higher in certain populations due to founder effects. The highest reported prevalence is 1 per 239 people in Flores Island of the Azores Islands, Portugal (Bettencourt and Lima. 2011. PubMed ID: 21635785).
Nearly all MJD/SCA3 patients demonstrate progressive cerebellar ataxia with dysarthria, ophthalmologic involvement, and vestibular dysfunction. Other variable features can also present in affected individuals and can be variable even within families (Colomer Gould. 2012. PubMed ID: 22451301). Motor neuron degeneration, mood changes, dystonia, parkinsonism, autonomic dysfunction, sleep disorders, restless legs syndrome, fatigue, and chronic pain have been commonly reported. Less frequent features that have been reported include cognitive difficulties, behavioral disorders, and respiratory involvement (Paulson and Shakkottai. 2020. PubMed ID: 20301375). Individuals with repeats in the intermediate range (45-59 repeats) may manifest with mild ataxia and/or restless legs syndrome (Paulson. 2012. PubMed ID: 21827905).
Age of onset of MJD/SCA3 ranges can be variable, commonly ranging from the second to fifth decades, though onset as late as 70 years has been reported (Paulson. 2012. PubMed ID: 21827905). There is an inverse correlation between the size of the polyglutamine tract size and age of onset (i.e., larger repeat sizes are associated with earlier disease onset). The largest reported expansions (86 and 83 repeats) have been reported to have childhood onset (5 and 11 years, respectively; Paulson and Shakkottai. 2020. PubMed ID: 20301375). MJD/SCA3 demonstrates anticipation in families, the phenomenon where each successive generation has earlier disease onset due to an increase in repeat size (Paulson. 2012. PubMed ID: 21827905).
To date, more than 30 genetically distinct forms of spinocerebellar ataxia have been described in OMIM. Since these diseases are difficult to distinguish due to overlapping clinical features, it is imperative to utilize molecular testing to establish a diagnosis. Testing for MJD/SCA3 is advantageous in individuals with spinocerebellar ataxia symptoms or with a known or suspected family history of autosomal dominant ataxia. Results from testing can help determine disease prognosis and guide treatment plans to reduce or prevent symptoms.
Genetics
Expansion of the CAG repeat within exon 10 of the ATXN3 gene is the only known cause of Machado-Joseph disease/spinocerebellar ataxia type 3 (Paulson and Shakkottai. 2020. PubMed ID: 20301375). MJD/SCA3 demonstrates autosomal dominant inheritance and complete penetrance in individuals with a pathogenic expansion (60 or more repeats). Normal alleles contain up to 44 CAG repeats. Individuals with an intermediate expansion (45 to 59 repeats) may have no clinical phenotype or mild clinical features (such as mild ataxia or restless legs syndrome); however, the offspring of these individuals are at an increased risk for inheriting a pathogenic expansion (Paulson and Shakkottai. 2020. PubMed ID: 20301375).
Sporadic (i.e., de novo) pathogenic expansions of the CAG repeat in ATXN3 are rare. This has been attributed to the fact that there is a relatively large difference in the repeat range for normal versus pathogenic repeats, especially compared to other diseases caused by poly-glutamine tract expansion (Paulson. 2012. PubMed ID: 21827905). For individuals with no apparent family history, it is most likely that one of their parents possessed an expansion in the intermediate range.
ATXN3 encodes a nuclear deubiquitinase enzyme with roles in transcription repression and protein homeostasis (Zeng et al. 2020. PubMed ID: 32982735). Multiple animal models, including mouse, Drosophila, and marmoset, have been generated to study MJD/SCA3 disease onset and progression (Colomer Gould. 2012. PubMed ID: 22451301; Xu et al. 2015. PubMed ID: 26257024; Tomioka et al. 2020. PubMed ID: 33071733). The ATXN3 gene is not considered essential for viability in human tissue culture cell lines (Gurumayum et al. 2021. PubMed ID: 33084874).
Clinical Sensitivity - Repeat-Primed PCR & Fragment Length
This test for repeat expansions in ATXN3 has approximately 100% clinical sensitivity for detection of MJD/SCA3 (Paulson and Shakkottai. 2020. PubMed ID: 20301375).
Testing Strategy
This test is designed to only detect pathogenic expansions of a poly-glutamine CAG repeat in exon 10 of the ATXN3 gene but does not assess for CAA interruptions. Our assay involves two amplicon-length assays from both the 3’ and 5’ ends of the repeat region to determine lengths of repeats. We are confident in our ability to detect expansions of 80 repeats and below. We have not tested our assays using samples with greater than 80 repeats, and therefore will report any expansion greater than 80 repeats as an expanded allele (>80 repeats) at this time.
Indications for Test
Testing for the ATXN3 repeat expansion is recommended for individuals suspected of having MSCA3 (presentation of progressive cerebellar ataxia and variable findings such as pyramidal and extra-pyramidal signs, peripheral amyotrophy, generalized areflexia, progressive external ophthalmoplegia, facial and lingual muscle twitches, and bulging eyes). Testing is also recommended for individuals with a family history of ataxia consistent with autosomal dominant inheritance.
Testing for the ATXN3 repeat expansion is recommended for individuals suspected of having MSCA3 (presentation of progressive cerebellar ataxia and variable findings such as pyramidal and extra-pyramidal signs, peripheral amyotrophy, generalized areflexia, progressive external ophthalmoplegia, facial and lingual muscle twitches, and bulging eyes). Testing is also recommended for individuals with a family history of ataxia consistent with autosomal dominant inheritance.
Gene
| Official Gene Symbol | OMIM ID |
|---|---|
| ATXN3 | 607047 |
| Inheritance | Abbreviation |
|---|---|
| Autosomal Dominant | AD |
| Autosomal Recessive | AR |
| X-Linked | XL |
| Mitochondrial | MT |
Disease
| Name | Inheritance | OMIM ID |
|---|---|---|
| Azorean Disease | AD | 109150 |
Citations 
- Bettencourt and Lima. 2011. PubMed ID: 21635785
- Colomer Gould. 2012. PubMed ID: 22451301
- Gurumayum et al. 2021. PubMed ID: 33084874
- Paulson and Shakkottai. PubMed ID: 20301375
- Paulson. 2012. PubMed ID: 21827905
- Ruano et al. 2014. PubMed ID: 24603320
- Tomioka et al. 2020. PubMed ID: 33071733
- Xu et al. 2015. PubMed ID: 26257024
- Zeng et al. 2020. PubMed ID: 32982735
Ordering/Specimens 
Ordering Options
We offer several options when ordering sequencing tests. For more information on these options, see our Ordering Instructions page. To view available options, click on the Order Options button within the test description.
myPrevent - Online Ordering
- The test can be added to your online orders in the Summary and Pricing section.
- Once the test has been added log in to myPrevent to fill out an online requisition form.
- PGnome sequencing panels can be ordered via the myPrevent portal only at this time.
Requisition Form
- A completed requisition form must accompany all specimens.
- Billing information along with specimen and shipping instructions are within the requisition form.
- All testing must be ordered by a qualified healthcare provider.
For Requisition Forms, visit our Forms page
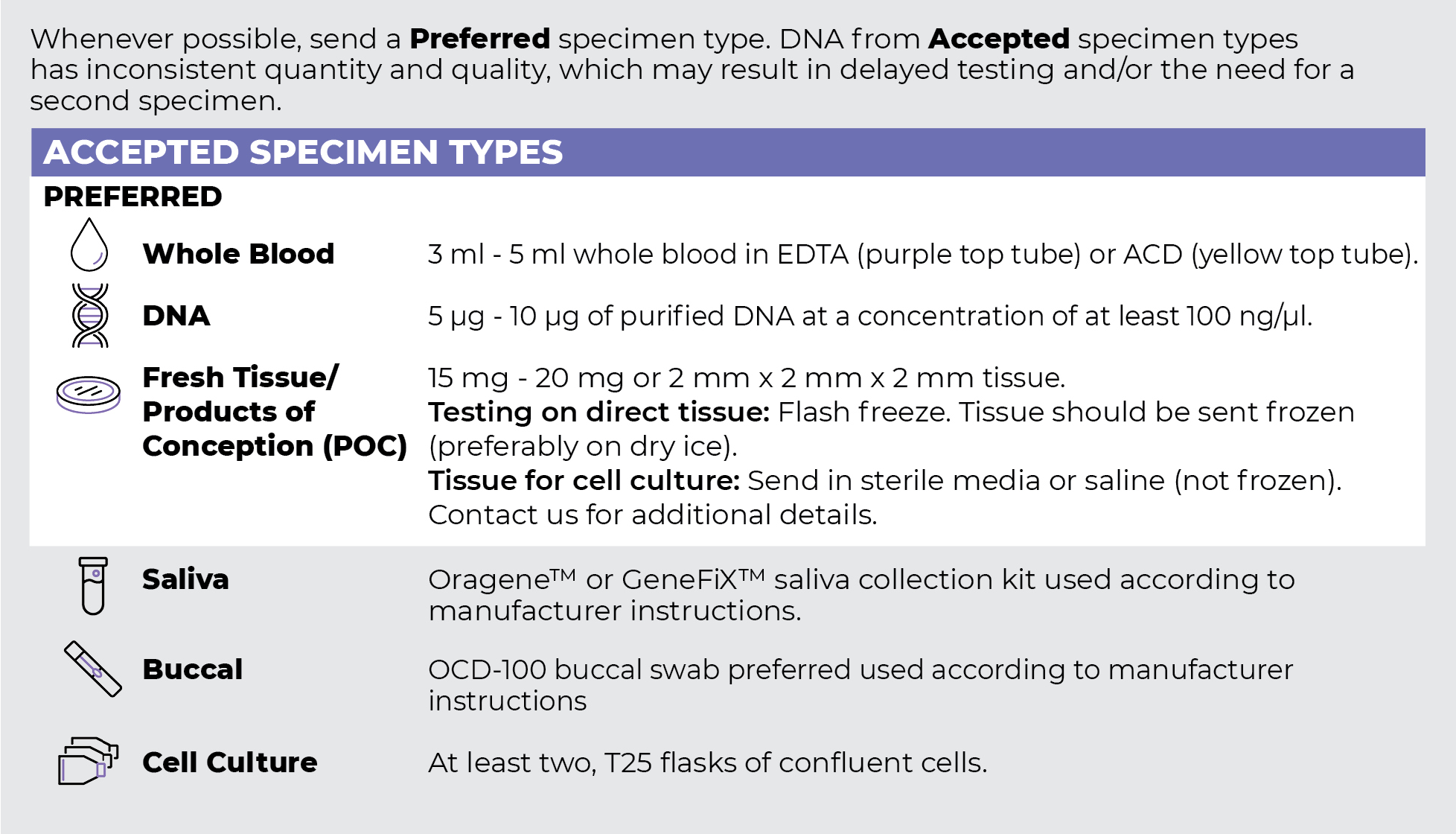
Specimen Types
Specimen Requirements and Shipping Details
ORDER OPTIONS
View Ordering Instructions1) Select Test Type
2) Select Additional Test Options
No Additional Test Options are available for this test.

